Innovation: How World Vision Rwanda transformed fleet management

Delivering humanitarian and development programs across Rwanda requires more than strategy and partnerships. It requires movement, often across long distances, challenging terrain, and dispersed communities. For World Vision Rwanda, vehicles are essential operational assets that enable staff to deliver programmes to dispersed, often hard-to-reach communities.
But managing a large fleet comes with risks!
Fleet vehicles represent one of the organisation’s highest operational costs. For years, fuel consumption and vehicle usage were tracked manually. Logs were maintained, but verification was limited. While there were concerns about excessive fuel consumption and possible unauthorised vehicle use, evidence was often insufficient to take corrective action.
The result was a familiar challenge in many organisations: suspicion without proof, policies without enforcement, and limited visibility into actual fleet behavior.
Leadership recognised that without stronger controls, the organisation faced ongoing financial inefficiencies, governance risks, and potential audit exposure.
Introducing Digital Oversight
Image of our Fleet Management System
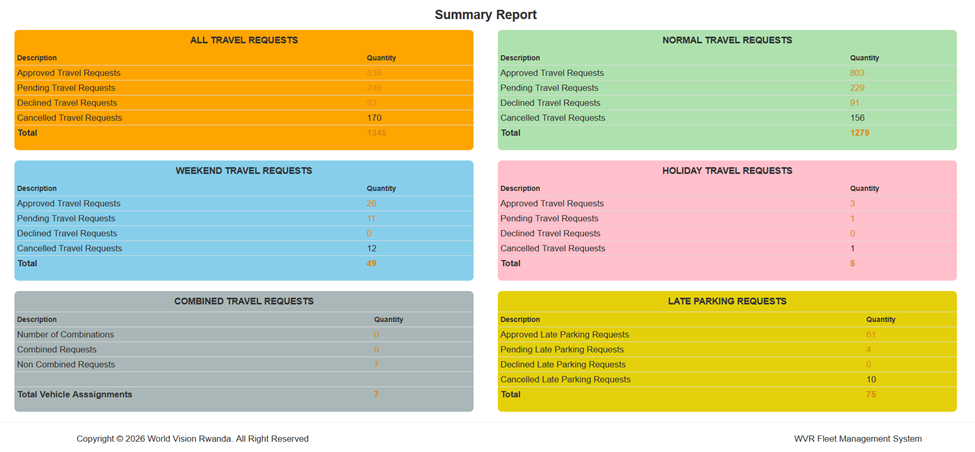
To address these gaps, World Vision Rwanda implemented a Fleet Management System designed to provide real-time, data-driven oversight of vehicle operations.
The system digitally tracks vehicle movements, fuel consumption, trip purpose, and usage patterns. Each vehicle is linked to authorised drivers and official assignments. Trip data and fuel records are automated, standardised, and visible to operational managers and leadership.
This shift transformed fleet management from manual record-keeping to active, evidence-based oversight.
According to Keith Bunyenyezi, the Head of IT and Digital Solutions at World Vision Rwanda, “Technology works best when it solves a real problem. In this case, the Fleet Management System addressed both cost leakage and weak controls. The results show that governance improves when transparency is built into daily operations.”
He further mentioned that the fleet Management System shifted World Vision Rwanda from reactive reporting to proactive control. By integrating vehicle telemetry, fuel analytics, and driver authorisation mapping, the organisation created a traceable ecosystem where misuse and inefficiency are no longer hidden variables.
Measurable change in fuel Consumption
The introduction of real-time monitoring immediately changed behavior.
Driving patterns, unnecessary trips, and delayed maintenance issues that previously went unnoticed became visible. Managers were able to identify inefficiencies and take corrective action based on verified data rather than assumptions.
As transparency increased, discipline followed. Drivers became more conscious of fuel use, and managers strengthened oversight.
Within months of implementation, average monthly fuel consumption reduced by a huge percentage, and monthly fuel costs decreased. These reductions reflect not just cost savings but improved operational efficiency and stronger stewardship of donor resources.
The system also significantly reduced unauthorised use of vehicles.
Previously, ambiguity around trip purpose and timing made it difficult to verify whether vehicle use aligned with official assignments. With digital tracking in place, vehicle movements became fully traceable and auditable.
Transparency alone proved to be a powerful deterrent. When trip records and usage patterns are visible and reviewable, misuse becomes harder to justify and easier to address.
The result was a marked decline in personal or unauthorised vehicle use, strengthening accountability across the organisation. While fuel savings are measurable, the broader impact is governance.
The Fleet Management System reduced operational risk, strengthened internal controls, and reinforced consistent policy enforcement. It shifted fleet oversight from trust-based assumptions to evidence-based management.
For World Vision Rwanda’s Global Technology & Digital (GTD) team, the initiative represents a technical upgrade but also demonstrates how technology can address real behavioral and governance challenges when aligned with organisational priorities.
By reducing fuel consumption and minimising vehicle misuse, World Vision Rwanda has strengthened cost control, accountability, and compliance. This is an operational improvement, as well as a systems upgrade, which protects resources, enhances stewardship, and ensures that vehicles serve their intended purpose, enabling impact for children and communities across Rwanda.
By Kellen Tumusiime, Business & Digital Workplace Analyst, WV Rwanda