Nurturing Care Groups (NCGs)
Nurturing Care Groups
Nurturing Care Groups (NCGs) are a behaviour change model designed to improve infant and young child feeding (IYCF), home care practices, care-seeking for sick children, and disease prevention. By mobilising trained community volunteers to reach caregivers with key health and nutrition messages, NCGs foster sustainable behaviour change at the household level. They can be implemented as a standalone approach or integrated with other core project models to achieve measurable, multi-sectoral impact.
What is the NCG Core project model?
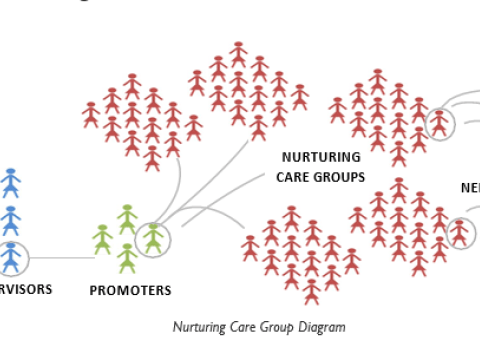
The Nurturing Care Group (NCG) model mobilises 10 to 15 volunteer behaviour change agents per group. These volunteers are selected by local households and trained every two weeks by project staff or government Community Health Workers (CHWs).
After each training, volunteers cascade health and nutrition messages to caregiver groups at the neighbourhood level, using peer-to-peer communication, home visits, and small group meetings. This structure creates a multiplier effect, ensuring that all target households are reached consistently – typically every two weeks.
Key features
- Locally selected volunteers deliver behaviour change messages and support in their own communities.
- NCGs foster social cohesion and peer support, reinforcing new health behaviours and caregiving practices.
- The model connects communities to local leaders, faith actors, clinics, and government services, strengthening health systems and accountability.
- Behaviour change activities focus on IYCF, care-seeking for sick children, disease prevention, and responsive caregiving.
By using interpersonal communication and neighbour-to-neighbour contact, NCGs establish new community norms and ensure equitable outreach to every family in the target group.
Core Components of the NCG Core project model
The NCG CPM is grounded in established behavioural science and tailored for community-level impact across multiple sectors. Its core components are as follows:
1. Behaviour change foundations
The model draws on several well-established behaviour change theories:
- Health Belief Model
- Theory of Planned Behaviour
- Theory of Reasoned Action
- Trans-Theoretical (Stages of Change) Model
These frameworks acknowledge that people are at different stages of readiness to change. As such, NCG materials and lesson plans are designed to meet households where they are – using tailored, progressive messaging and reinforcement.
2. Modular, multisectoral curriculum
- The NCG CPM offers a flexible curriculum of 10 themed modules, each lasting 2–3 months and promoting 4–6 key behaviours.
- Modules cover key areas such as WASH, Health and Nutrition, Education, and Child Protection. (Livelihood topics may also be included where relevant.)
- The full curriculum includes 48 to 72 lessons, ideally delivered over a 24 to 36 month period, but adaptable for shorter project cycles.
3. Peer role modelling and early adopters
- Local female volunteers serve as both behaviour change agents and positive role models, encouraging adoption of key practices among neighbours.
- This peer-to-peer model leverages trust, shared experience, and visibility to shift community norms and drive sustained behaviour change.
4. Integrated, multisectoral impact
- The NCG model is built on evidence showing that multisectoral interventions – such as combining nutrition and early childhood stimulation – achieve better outcomes than siloed approaches.
- NCGs are particularly effective in addressing complex challenges like stunting, where factors from health, hygiene, nutrition, and caregiving intersect.